A Flange is a method of connecting pipes, valves, pumps and other equipment to form a piping system. It also provides easy access for cleaning, inspection or modification. Flanges are usually welded or screwed. Flanged joints are made by bolting together two flanges with a gasket between them to provide a seal. Pipe Flanges are the second most used joining method after welding in the industrial piping sector. They are used when joints need dismantling, providing flexibility for maintenance, connecting the pipe with various equipment and valves. Breakup Flanges are added to the pipeline system if regular maintenance is required during normal plant operation. A Flanged joint comprises of three components; flange; gasket; and bolting the assembly.
It is not advisable to use a Flange connection in underground piping when it is supposed to be buried as they can be the most common source of a leak and/or fire in a process plant. There are a variety of Flanges available to suit your requirements and National Pipeline Supplies can suppy or source all types. A Flange can be classified in several alternate ways based on the following:
- Types of Connection
- Flange Facing Types
- Pressure-Temperature Ratings
- Material Types
The main Flange Types are:
- Threaded Flanges
- Socket-Weld Flanges
- Slip-On Flanges
- Lap Joint Flanges
- Weld Neck Flanges
- Blind Flanges
- Reducing Flange
- Expander Flange
- Flangeolet / Weldoflange / Nippoflange
Threaded Flanges
A Threaded Flange is also known as a screwed Flange, and it is having a thread inside the Flange bore which fits on the pipe with a matching male thread on the pipe. This type of joint connection is speedy and simple but not suitable for high pressure and temperature applications. Threaded Flanges are mostly used in utility services such as air and water. (See image below)
- Is also available in limited Size of NPS 4” and below
- Threaded Flanges can be Flat Face or Rasied Face
- It is a Low-cost flange.
Threaded Flange
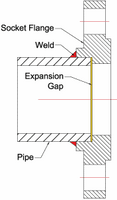
Socket-Weld Flanges
Socket-Weld Flanges has a female socket in which the pipe is fitted. Fillet welding is done from outside on the pipe. Generally, it is used in small bore piping and is only suitable for low pressure and temperature application.
- Socket-Welded Flanges can be Flat Face or Raised Face
- The cost of flange and fabrication is moderate
- You can see the Socket-Weld Flange welded with pipe in the cross section image below

Socket Weld Flange and Cross Section (Including Weld Detail)
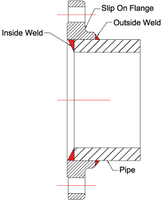
Slip-On Flanges
A Slip-On Flange has a hole with a matching outside diameter of pipe from which pipe can pass. The Flange is placed on pipe and fillet welded from both inside and outside. Slip-On Flange is suitable for low pressure and temperature application.
- This type of Flange available in large size also
- It can be Flat Face or Raised Face
- The cost of Flange and fabrication is moderate
- You can see the Slip-On Flange welded with pipe in the cross section image below

Slipon Flange Raised Face and Cross Section (Including Weld Detail)
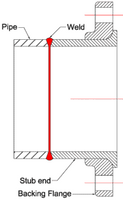
Lap Joint Flanges
Lap Joint Flanges have two components, a stub end, and a loose backing Flange. The stub end is Butt-Welded to the pipe, and the backing Flange freely moves over the pipe. The backing Flange can be of a different material than stub material and normally of carbon steel to save the cost. A Lap Joint Flange is used where frequent dismantling is required and space is constrained or confinded.
- This Flange provides better joining due to butt-weld as compared to a Socket and Threaded type Flanges
- Not suitable for small size, Costly components, and fabrication as compared to Threaded, Slip-On, and Socket Flange.
- You can see the Lap Joint Flange welded with pipe in the cross section image below.

Lap Flange with Stub & Hub and Cross Section (Including Weld Detail)
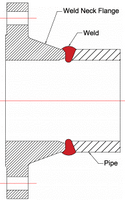
Weld Neck Flanges
A Weld Neck Flange is the most widely used type in process piping. It gives the highest level of joint integrity as it is Butt-Welded with a pipe. These types of Flanges are used in high pressure and temperature application. Weld Neck Flanges are Bulky & costly with respect to other types of Flanges.
- High skill is required for fabrication and also requires more space to accommodate the piping system due to the long hub.
- A weld Neck Flange is available in all sizes & it can be Flat Face, Raised Face or Ring Joint types.
- You can see the Weld Neck flange welded with pipe in the cross section image below.

Weld Neck Flange and Cross Section (Including Weld Detail)
Blind Flanges
The Blind Flange is a blank disc with bolt holes. These types of Flanges are used with another type of Flange to isolate the piping system or to terminate the piping as an end. Blind Flanges are also used as a manhole covers in a vessel. (See image below)
Blind Flange
Reducing Flange
A Reducing Flange is used in place of a standard Flange to allow for a change in pipe size. This Flange eliminates the need for a standard reducer in piping. The Flange consists of one specified diameter with a smaller diameter bore size. Except for the bore and hub dimensions, a Reducing Flange has dimensions of the standard pipe Flanges size and is considered an economical means to make a pipe size transition.
These Flanges are available in Weld Neck, Slip-On, and Threaded end types. Reducing Flanges are an economical way to make transitions between pipes of different sizes, however, due to high-pressure loss, they are rarely used in piping. (See image below)
Reducing Flange
Expander Flange
It is similar to a Weld Neck Flange but increases the size of the pipe to the first or second larger size. It is an alternative to using a reducer and Weld Neck Flange. Useful for connecting to valves, compressors, and pumps.
These Flanges are specially designed. Dimensions of the Weld Neck are in line with the connecting pipe, other dimensions are in accord with standard ASME B16.5 Flanges. (See image below)
Expander flange
Flangeolet / Weldoflange / Nippoflange
Flangeolet is a combination of Olet (mainly Weldolet or Nipple) and Flange. The hub length is longer like a long neck weld Flange. It is a 90 Degree branch connection use for high-pressure piping. It reduces the two weld joints than of the traditional Olet + Pipe + Flange connection and one weld joint in case of Olet + Flange connection. (See image below)
Flangeolet
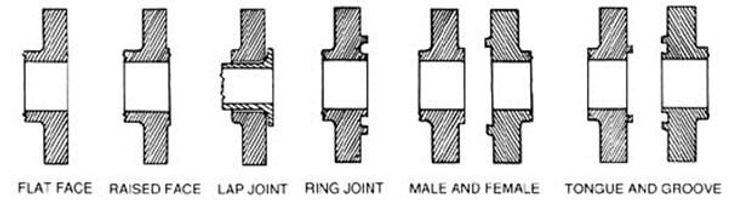
Flange Face Types
- Flat Face
- Raised Face
- Lap Joint
- Ring Joint
- Male and Female
- Tongue and Groove
Types of Flange Faces
Flat Face
As the name suggests, the Flat Face Flange has a flat face. Flat Face Flanges are used when the counter-Flanges are flat faces. This condition occurs mainly in connection to Cast Iron equipment, valves, and specialties. A full-face gasket is used when a Flat Face Flange is used.
Raised Face
Raised Face Flange has a small portion around the bore that is raised from the face. The gasket seats on this raised face. The height of the raised face depends on the Flange pressure-temperature rating that is known as a class of the Flange. For 150# & 300# height of the raised face is 1/6” and above 300# it is 1/4”. The inside bore circle type of gasket is used with a Raised Face Flange.
RTJ Face
Ring Joint Type Face Flange has a specially designed grove in which a metal gasket seats. This type of Flange is used in high pressure and temperature services.
Flat Face, Raised Face and Ring Type Joint Face (RTJ)
Flange Materials
Flanges are welded to the pipe and equipment nozzle. Usually manufactured from the following materials:
- Carbon steel
- Low alloy steel
- Stainless steel
- Combination of Exotic materials and other backing materials
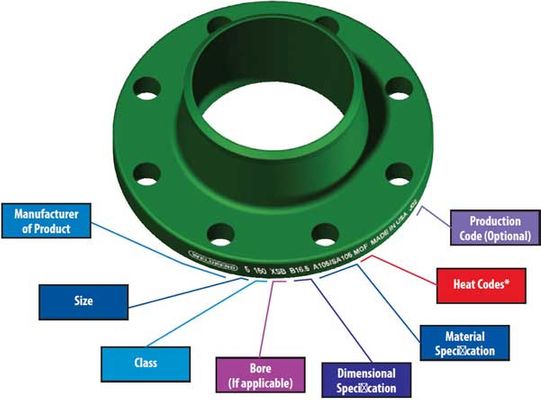
Marking on the Flange Body
Each piping component is marked for proper identification. Marking of Flanges must include the following so that during fabrication and post-fabrication it can be easily traced. (See image below)
- Manufacturer logo
- ASTM material code
- Material Grade
- Service rating (Pressure-temperature Class))
- Size
- Thickness (Schedule)
- Heat No
- Special marking if any QT (Quenched and tempered) or W (Repair by welding)
Flange Marking